Value investing in stocks involves a methodical approach to selecting undervalued stocks with long-term potential. As we delve into this topic, we explore the key principles, strategies, and criteria that define this investment strategy.
We’ll uncover the importance of fundamental analysis, stock selection criteria, risk management, and the debate between a long-term versus short-term perspective in value investing.
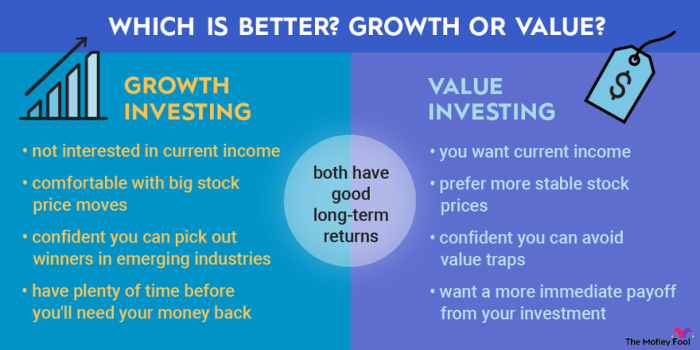
Overview of Value Investing
Value investing in stocks involves identifying undervalued companies in the market and investing in them with the expectation that their true worth will eventually be recognized by other investors, leading to a rise in stock prices. This strategy is based on the principle that the market sometimes undervalues quality companies, providing opportunities for long-term gains.
Value investors typically look for stocks trading at a discount to their intrinsic value, which can be determined through fundamental analysis of factors such as earnings, cash flow, and assets. By focusing on the underlying value of a company rather than short-term market trends, value investors aim to achieve above-average returns over time.
Principles of Value Investing
- Buy low and sell high: Value investors seek to purchase stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value, offering a margin of safety.
- Focus on fundamental analysis: Instead of following market trends or speculation, value investors analyze financial statements and business fundamentals to assess the true value of a company.
- Patience and discipline: Value investing requires a long-term perspective, as it may take time for the market to recognize the true worth of a undervalued stock.
Well-Known Value Investors and Their Strategies
- Warren Buffett: Perhaps the most famous value investor, Buffett follows a disciplined approach of buying quality companies with strong competitive advantages at attractive prices.
- Benjamin Graham: Known as the “father of value investing,” Graham developed the principles of value investing and authored the classic book “The Intelligent Investor.”
- Seth Klarman: Klarman is a respected value investor known for his focus on margin of safety and risk management in his investment decisions.
Fundamental Analysis in Value Investing

Fundamental analysis plays a crucial role in value investing as it involves evaluating the financial health and performance of a company to determine its intrinsic value. This method focuses on analyzing key financial metrics and ratios to identify undervalued stocks that have the potential for long-term growth.
Key Financial Metrics in Value Investing
Fundamental analysis in value investing involves looking at various financial metrics to assess the true worth of a company. Some key metrics that value investors typically consider include:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: This ratio helps investors understand how much they are willing to pay for a company’s earnings. A low P/E ratio may indicate an undervalued stock.
- Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: The P/B ratio compares a company’s market value to its book value, providing insight into whether a stock is undervalued relative to its assets.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio shows the amount of debt a company has relative to its equity. A lower debt-to-equity ratio is typically preferred by value investors.
- Free Cash Flow: Evaluating a company’s free cash flow helps investors understand how much cash the business generates after accounting for capital expenditures.
- Dividend Yield: Value investors often look for stocks with a stable dividend yield, as it can provide a source of income and potentially indicate a company’s financial stability.
Importance of Intrinsic Value in Value Investing
Intrinsic value is a key concept in value investing, representing the true worth of a company’s stock based on its fundamentals. Value investors seek to identify stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value, believing that these undervalued stocks have the potential for significant price appreciation in the future. By focusing on intrinsic value, investors aim to buy stocks at a discount to their true worth, maximizing their potential returns over time.
Stock Selection Criteria for Value Investing: Value Investing In Stocks

Value investing involves selecting stocks based on specific criteria that indicate the potential for long-term growth and profitability. These criteria are fundamental to the value investing approach and help investors identify undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.
Comparison of Value Investing Criteria with Other Approaches
When compared to other investment approaches like growth investing or momentum investing, value investing focuses on finding stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value. This means that value investors look for companies that are priced lower than their true worth, based on factors such as earnings, book value, and cash flow. In contrast, growth investors prioritize companies with high growth potential, while momentum investors focus on stocks that are trending upwards in the market.
Examples of Companies that Typically Fit Value Investing Criteria
Some examples of companies that often meet the criteria for value investing include established companies with stable earnings, low debt levels, and consistent dividend payouts. Companies in industries that are currently out of favor with the market but have strong long-term prospects can also be attractive to value investors. For instance, companies in the energy sector or traditional manufacturing industries may fit the bill for value investing, as they may be undervalued due to temporary market conditions.
Risk Management in Value Investing
Risk management plays a crucial role in value investing as it helps investors protect their capital and maximize returns. Value investors focus on identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, but they also need to consider the risks associated with their investment decisions.
Role of Risk Management in Value Investing
Value investors mitigate risks in their investment decisions through various strategies:
- Diversification: Value investors spread their investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographies to reduce the impact of a single investment’s performance on their overall portfolio.
- Margin of Safety: Value investors look for stocks trading below their intrinsic value to build a margin of safety. This approach helps protect against potential downside risks.
- Long-Term Perspective: Value investors focus on the long-term prospects of a company rather than short-term market fluctuations. This approach allows them to ride out market volatility and reduce the impact of short-term risks.
- Exit Strategy: Value investors have a predefined exit strategy in place to manage risks effectively. They set target prices for their investments and sell when the stock reaches a certain valuation.
Strategies for Minimizing Risk in Value Investing, Value investing in stocks
- Conduct Thorough Research: Value investors perform detailed fundamental analysis to understand the financial health and prospects of a company before making investment decisions. This research helps identify potential risks and opportunities.
- Focus on Quality: Value investors prioritize companies with strong competitive advantages, solid balance sheets, and consistent earnings growth. Investing in high-quality companies reduces the risk of permanent capital loss.
- Monitor Portfolio Regularly: Value investors regularly review their portfolio to assess the performance of their investments and make necessary adjustments. This proactive approach helps identify and address potential risks in a timely manner.
- Stay Disciplined: Value investors stick to their investment principles and remain disciplined in their approach, even during periods of market volatility. This discipline helps avoid impulsive decisions driven by emotions and minimizes risks in the long run.
Long-term vs. Short-term Perspective

When it comes to value investing, investors can choose between a long-term or short-term perspective to achieve their financial goals. Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, depending on the investor’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment objectives.
Long-term Perspective
A long-term perspective in value investing involves holding onto investments for an extended period, typically years or even decades. This approach focuses on the intrinsic value of a stock and the company’s fundamentals, allowing investors to ride out market fluctuations and benefit from compounding returns over time.
- Advantages:
- Less susceptible to short-term market volatility
- Opportunity to benefit from the company’s long-term growth potential
- Lower transaction costs and taxes due to less frequent trading
- Disadvantages:
- Requires patience and discipline to hold onto investments during market downturns
- Potential opportunity cost of missing out on short-term gains
- Market conditions may change, affecting the investment thesis over time
Short-term Perspective
On the other hand, a short-term perspective in value investing involves buying and selling stocks within a shorter time frame, often based on market trends, technical analysis, or short-term catalysts. This approach aims to capitalize on short-term price movements to generate quick profits.
- Advantages:
- Potential for quick gains in a short period of time
- Flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions and opportunities
- Ability to take advantage of short-term mispricing in the market
- Disadvantages:
- Higher risk due to market volatility and uncertainty
- Increased transaction costs and taxes from frequent trading
- Lack of focus on underlying fundamentals and long-term value creation
Successful value investors like Warren Buffett and Benjamin Graham have predominantly adopted a long-term perspective in their investment approach. They emphasize the importance of patience, discipline, and focusing on the intrinsic value of a company rather than short-term price movements. On the other hand, there are traders like George Soros who have achieved success with a short-term perspective, leveraging market trends and short-term opportunities to generate profits.
In conclusion, value investing in stocks offers a disciplined approach to navigating the stock market, focusing on intrinsic value and long-term growth potential. By understanding the core concepts and strategies discussed, investors can make informed decisions to build a successful investment portfolio.
Are you interested in learning about the stock market for beginners ? Understanding the basics of investing in stocks can be overwhelming at first, but with the right guidance, you can navigate through the complexities and start building your portfolio. By grasping the fundamentals of the market, you can make informed decisions and potentially grow your wealth over time.
If you’re looking to delve deeper into understanding the stock market , it’s essential to comprehend how it functions and what factors influence its fluctuations. By educating yourself on key concepts such as market trends, company performance, and economic indicators, you can develop a strategic approach to investing that aligns with your financial goals.
For those interested in exploring stock trading for beginners , it’s important to learn about different trading strategies, risk management techniques, and market analysis tools. By honing your skills in trading, you can maximize your profits and minimize potential losses in the volatile world of stock trading.