With Growth vs value stocks at the forefront, this article delves into the intriguing world of investment, shedding light on the differences between these two types of stocks and guiding readers through the complexities of the market.
Growth vs Value Stocks Overview

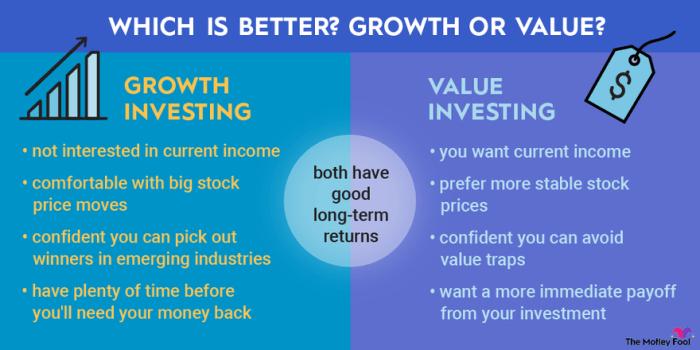
In the world of investing, growth and value stocks represent two different approaches to building a portfolio. Growth stocks are companies that are expected to grow at a rate higher than the market average, often reinvesting their earnings into expansion. On the other hand, value stocks are companies that are considered undervalued by the market, trading at a lower price compared to their intrinsic value.
The main differences between growth and value stocks lie in their investment strategies and the characteristics of the companies they represent. Growth stocks are typically associated with higher volatility and valuations, as investors are willing to pay a premium for the potential of future growth. In contrast, value stocks are often viewed as safer investments, with lower valuations and more stable returns.
Examples of well-known growth stocks include technology giants like Amazon, Facebook, and Tesla, which have shown rapid revenue growth and innovation. In comparison, value stocks such as Coca-Cola, Johnson & Johnson, and Berkshire Hathaway are known for their long-standing presence in the market and stable dividend payouts.
Growth Stocks
Growth stocks are typically characterized by their high earnings growth potential, often driven by new products or services, market expansion, or disruptive technologies. Investors in growth stocks are willing to pay a premium for these growth prospects, even if it means accepting higher volatility and lower dividend yields.
- Amazon: The e-commerce giant has consistently delivered strong revenue growth driven by its diverse product offerings and expanding cloud services.
- Tesla: Known for its innovative electric vehicles and energy products, Tesla is a prime example of a growth stock with a focus on disrupting traditional industries.
- Facebook: The social media company continues to grow its user base and advertising revenue, making it a popular choice among growth investors.
Value Stocks
Value stocks, on the other hand, are often overlooked by the market, leading to their undervaluation. These stocks are typically associated with stable cash flows, solid balance sheets, and dividends, making them attractive to investors seeking a more conservative approach to investing.
- Coca-Cola: As a well-established beverage company, Coca-Cola is considered a value stock due to its stable revenue streams and long history of dividend payments.
- Johnson & Johnson: A leader in the healthcare industry, Johnson & Johnson is known for its diversified product portfolio and consistent performance, appealing to value investors.
- Berkshire Hathaway: Warren Buffett’s conglomerate is a classic example of a value stock, focusing on acquiring undervalued companies with strong fundamentals for long-term growth.
Characteristics of Growth Stocks

Growth stocks are typically companies that are expected to grow at a rate significantly above average compared to other companies in the market. Investors are attracted to growth stocks because of their potential for high returns, driven by strong revenue and earnings growth.
Revenue Growth
One of the key characteristics of growth stocks is their ability to consistently grow their revenue at a rapid pace. This growth is often the result of innovative products or services, expanding market share, or successful marketing strategies.
Earnings Growth, Growth vs value stocks
In addition to revenue growth, growth stocks also demonstrate strong earnings growth. These companies are able to convert their revenue into profits efficiently, leading to a positive impact on their stock prices.
High Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
Investors often look for growth stocks with high price-to-earnings ratios, as this indicates that the market is willing to pay a premium for the company’s growth potential. While a high P/E ratio can signal overvaluation, it is a common characteristic of growth stocks.
Low Dividend Yield
Growth stocks typically reinvest a significant portion of their earnings back into the business for future growth opportunities. As a result, these companies often have low or no dividend yield, as they prioritize growth over distributing profits to shareholders.
Risk Factors
While growth stocks offer the potential for high returns, they also come with certain risks. These include high volatility, as the stock prices of growth companies can fluctuate significantly in response to market conditions. Additionally, there is a risk of overvaluation, where investors may pay a premium for growth that is not sustainable in the long run.
Characteristics of Value Stocks

Value stocks are typically characterized by the following traits that differentiate them from growth stocks:
1. Undervaluation
Value stocks are considered undervalued compared to their intrinsic value. This means that the stock price may not reflect the true worth of the company based on fundamental factors such as earnings, assets, or cash flow.
2. Low Price-to-Earnings Ratio
Investors often look for value stocks with low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios. A low P/E ratio indicates that the stock is trading at a lower price relative to its earnings, making it potentially attractive for value investors.
3. Dividend Yield
Value stocks may offer higher dividend yields compared to growth stocks. Companies that pay dividends regularly and have a history of stable or increasing dividend payments are often favored by value investors seeking income.
4. Strong Financials
Value stocks are usually associated with companies that have solid financial fundamentals, including low debt levels, consistent revenue growth, and healthy profit margins. These factors contribute to the perceived stability and value of the stock.
5. Contrarian Investing
Value investing often involves a contrarian approach, where investors go against the market consensus and seek opportunities in stocks that are temporarily out of favor or overlooked by the broader market. This contrarian mindset can lead to identifying undervalued gems in the market.
6. Margin of Safety
Value investors typically look for a margin of safety when investing in value stocks. This concept involves buying a stock at a significant discount to its intrinsic value to protect against downside risk and potential losses.
Investing in value stocks comes with its own set of risk factors, including:
Risk Factors
- Value traps: Some value stocks may appear cheap for a reason, such as poor business prospects or industry headwinds, leading investors into value traps.
- Market timing: Timing the market to buy undervalued stocks at the right time can be challenging and requires careful analysis.
- Value decay: Value stocks may take longer to realize their true worth, and the market may not recognize their value for an extended period, leading to potential underperformance.
- Macroeconomic risks: Value stocks may be more sensitive to economic downturns or industry-specific challenges, exposing investors to higher volatility and risk.
Performance Comparison
Historically, growth stocks have outperformed value stocks in terms of returns. This is because growth stocks are associated with companies that are experiencing rapid revenue and earnings growth, making them more attractive to investors seeking high returns. On the other hand, value stocks are often overlooked by investors and may be undervalued, leading to lower returns compared to growth stocks.
Historical Performance
Growth stocks have shown higher returns compared to value stocks over the long term. For example, over the past decade, growth stocks have significantly outperformed value stocks, especially in sectors like technology and healthcare. This can be attributed to the strong earnings growth and market demand for innovative products and services offered by growth companies.
Performance in Different Market Conditions
The performance of growth and value stocks can vary depending on market conditions. In bull markets, growth stocks tend to perform well as investors are willing to pay a premium for high-growth companies. Conversely, in bear markets or during economic downturns, value stocks may outperform growth stocks as investors seek safe-haven assets with stable dividends and lower valuations.
Factors Influencing Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of growth and value stocks. For growth stocks, factors like technological advancements, market trends, and company-specific growth prospects play a significant role in driving returns. On the other hand, value stocks are influenced by factors such as economic conditions, interest rates, and overall market sentiment towards undervalued companies.
Investment Strategies
When it comes to investing in growth and value stocks, different strategies are employed based on the characteristics of each type of stock. Understanding these strategies is crucial for investors looking to optimize their portfolios.
Investment Strategies for Growth Stocks
Investing in growth stocks typically involves focusing on companies that are expected to experience rapid earnings growth in the future. Here are some common strategies used for investing in growth stocks:
- Identifying companies with high revenue and earnings growth potential.
- Looking for companies in high-growth industries such as technology or healthcare.
- Emphasizing future potential over current valuation metrics.
- Being willing to pay a premium for stocks with strong growth prospects.
Investment Strategies for Value Stocks
Value investing focuses on finding undervalued stocks that have the potential to increase in price over time. Here are some strategies commonly used for investing in value stocks:
- Searching for stocks trading below their intrinsic value.
- Looking for companies with strong fundamentals but low stock prices.
- Emphasizing metrics like price-to-earnings ratio and price-to-book ratio.
- Being patient and waiting for the market to recognize the true value of the stock.
Comparison of Investment Strategies
When comparing the strategies used for investing in growth versus value stocks, it’s important to note the following:
- Growth stock investors focus on future potential and are willing to pay a premium for high-growth companies.
- Value stock investors emphasize current valuation metrics and look for bargains in the market.
- Growth investing tends to be more speculative and volatile, while value investing is often seen as a more conservative approach.
- Both strategies can be successful depending on market conditions and individual risk tolerance.
Market Trends
Market trends play a crucial role in shaping the performance of growth and value stocks. Understanding the current market trends and predicting future movements can help investors make informed decisions regarding their investment strategies.
Current Market Trends
- Technology Dominance: In recent years, technology stocks have dominated the market, driving growth stock performance.
- Inflation Concerns: Rising inflation rates have led to a shift towards value stocks as investors seek more stable investments.
- Economic Recovery: With the global economy recovering from the impacts of the pandemic, growth stocks in sectors like e-commerce and healthcare continue to thrive.
Impact on Growth and Value Stocks
- Volatility: Market trends can create volatility in stock prices, impacting both growth and value stocks.
- Investor Sentiment: Changing market trends can influence investor sentiment towards different types of stocks, affecting their performance.
- Rotation Strategies: Investors may adjust their portfolios based on market trends, rotating between growth and value stocks to capitalize on opportunities.
Predictions for Future Market Trends
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can significantly impact growth and value stocks, with rising rates potentially favoring value stocks.
- Regulatory Environment: Shifts in regulations can impact sectors differently, leading to changes in market trends for growth and value stocks.
- Global Events: Geopolitical events and global economic conditions can shape future market trends, influencing the performance of different types of stocks.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics between growth and value stocks is essential for making informed investment decisions in today’s ever-changing market landscape. Keep these insights in mind as you navigate your investment journey.
When it comes to investing in stocks, diversification is key to managing risk and maximizing returns. Learn how to diversify your stock portfolio by spreading your investments across different industries, sectors, and asset classes. This strategy can help protect your portfolio from market volatility and potential losses.
Understanding stock charts is essential for making informed investment decisions. By learning how to read stock charts , you can analyze price movements, identify trends, and determine the best time to buy or sell stocks. Technical analysis can provide valuable insights into market behavior and help you stay ahead of the curve.
Implementing dollar-cost averaging in your stock investments can help reduce the impact of market fluctuations and minimize emotional decision-making. By regularly investing a fixed amount over time, you can benefit from market volatility and potentially lower your average cost per share. Discover the benefits of dollar-cost averaging in stocks and take control of your investment strategy.