Delving into Dollar-cost averaging in stocks, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with a focus on how this strategy can benefit investors looking to build wealth over time. As we explore the ins and outs of dollar-cost averaging, you’ll gain valuable insights into how to navigate the stock market with a steady and disciplined approach.
Exploring the intricacies of implementing this strategy and the importance of monitoring and adjusting your investments, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your financial future.
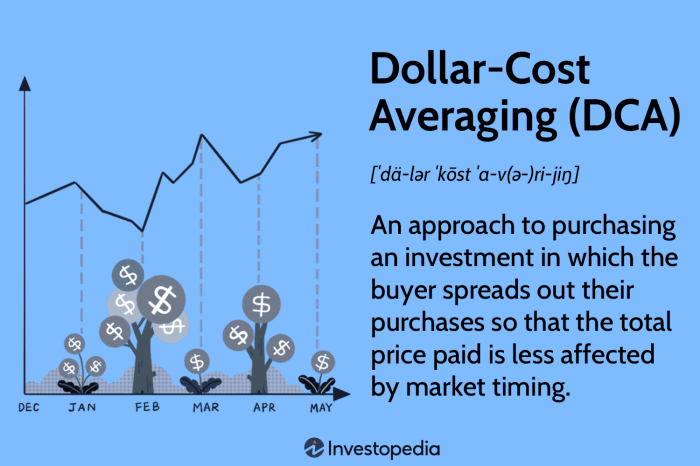
Definition of Dollar-Cost Averaging: Dollar-cost Averaging In Stocks

Dollar-cost averaging is an investment strategy where an investor regularly buys a fixed dollar amount of a particular investment, regardless of the share price. This approach helps to reduce the impact of market volatility on the overall purchase price, as more shares are acquired when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high.
How Dollar-Cost Averaging Works
When an investor decides to invest $100 every month in a specific stock, they will purchase more shares when the price is low and fewer shares when the price is high. For example, if the stock is priced at $10 one month, the investor will buy 10 shares. If the price increases to $20 the following month, the investor will only purchase 5 shares. Over time, this strategy helps to average out the cost of acquiring shares.
Benefits of Using Dollar-Cost Averaging
- Reduces the impact of market volatility: By consistently investing a fixed amount, investors avoid making emotional decisions based on market fluctuations.
- Allows for automatic investing: Dollar-cost averaging enables investors to automate their investment process, making it a convenient and disciplined approach.
- Potential for long-term gains: Over time, dollar-cost averaging can lead to a lower average cost per share, potentially increasing overall returns.
Implementing Dollar-Cost Averaging
When it comes to implementing dollar-cost averaging in stocks, it is crucial to follow a systematic approach to maximize its benefits and reduce risks. Below are some step-by-step guidelines and best practices to help you get started:
Setting Up a Dollar-Cost Averaging Plan
- Choose the Frequency: Decide how often you want to invest in stocks. It can be weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly.
- Select the Investment Amount: Determine how much money you can afford to invest consistently.
- Choose the Stocks: Select the stocks or ETFs you want to invest in. Ensure they align with your investment goals.
- Open a Brokerage Account: To start investing, you need to open a brokerage account that allows you to buy stocks.
- Automate the Process: Set up automatic transfers from your bank account to your brokerage account to ensure regular investments.
Best Practices for Dollar-Cost Averaging
- Stay Consistent: Stick to your investment schedule regardless of market fluctuations.
- Focus on the Long-Term: Dollar-cost averaging works best when you have a long-term investment horizon.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your investments across different sectors or asset classes to reduce risk.
- Monitor Your Progress: Regularly review your investment performance and make adjustments if needed.
Comparing Different Approaches
- Fixed Amount vs. Fixed Units: You can either invest a fixed amount of money each time or a fixed number of shares/units.
- Single Stock vs. ETFs: Decide whether you want to invest in individual stocks or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) for diversification.
- Market Timing vs. Regular Investing: Dollar-cost averaging involves regular investing without trying to time the market.
- Rebalancing vs. Holding: Consider whether you want to rebalance your portfolio periodically or hold onto your investments for the long term.
Monitoring and Adjusting
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Dollar-Cost-Averaging-DCA-f79fcd89eaa34bb7adad3dacc3129798.png?w=700)
When implementing a dollar-cost averaging strategy in stocks, it is crucial to monitor its performance regularly to ensure that it aligns with your investment goals. This involves tracking the overall returns, analyzing the market trends, and evaluating the effectiveness of your strategy over time.
Monitoring the Performance, Dollar-cost averaging in stocks
- Regularly review your investment portfolio to track the performance of individual stocks.
- Compare the returns generated by your dollar-cost averaging strategy with a lump-sum investment approach to evaluate its efficiency.
- Use financial tools and software to monitor the market trends and adjust your investment strategy accordingly.
Adjusting Investment Amounts
- Consider increasing your investment amounts during market downturns to take advantage of lower stock prices.
- Reduce the investment amounts during periods of high market volatility to minimize potential losses.
- Rebalance your portfolio periodically to maintain a diversified asset allocation and optimize your returns.
Evaluating Effectiveness
- Track the overall performance of your dollar-cost averaging strategy compared to the benchmark indices to assess its effectiveness.
- Analyze the impact of external factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and industry trends on your investment returns.
- Seek professional financial advice to review your investment strategy and make necessary adjustments based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Risk Management in Dollar-Cost Averaging

When implementing dollar-cost averaging in stocks, it is crucial to have a solid risk management strategy in place to protect your investments. By understanding the risks associated with this investment approach, you can make informed decisions to mitigate potential downsides.
Strategies for Managing Risk
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and industries to reduce the impact of a single stock’s performance on your overall portfolio.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep a close eye on market trends, economic indicators, and company news to make timely adjustments to your investment strategy.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Implement stop-loss orders to automatically sell a stock if it reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
- Rebalancing: Periodically rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation and reduce exposure to overvalued or underperforming stocks.
Comparison with Lump-Sum Investing
- Risk Distribution: Dollar-cost averaging spreads the risk of investing over time, reducing the impact of market volatility on your portfolio compared to lump-sum investing.
- Market Timing: Lump-sum investing exposes you to the risk of making a large investment at an inopportune time, while dollar-cost averaging allows you to average out the impact of market fluctuations.
- Psychological Factors: Dollar-cost averaging can help investors avoid the regret of making a large investment just before a market downturn, providing a more disciplined approach to investing.
Impact of Market Volatility and Mitigating Risks
- Volatility Risk: Market fluctuations can impact the effectiveness of dollar-cost averaging, leading to potential losses if stock prices decline sharply.
- Long-Term Perspective: Maintain a long-term investment horizon to ride out short-term market volatility and benefit from the power of compounding returns over time.
- Staying Informed: Stay informed about market trends, economic developments, and company performance to make informed decisions and adjust your investment strategy accordingly.
In conclusion, Dollar-cost averaging in stocks offers a reliable way to grow your investment portfolio steadily over time. By following the best practices and staying vigilant in monitoring your investments, you can mitigate risks and maximize returns in the long run. Embrace the power of dollar-cost averaging and take control of your financial journey today.
For those looking to generate passive income, dividend investing in stocks is a popular strategy. By investing in companies that pay out dividends regularly, investors can enjoy a steady stream of income. This method is favored by those seeking long-term financial stability.
New to the world of investing? Understanding the basics of the stock market is crucial for success. Learning about different investment options, risk management, and market trends is essential for beginners. Check out this guide on stock market for beginners to kickstart your investment journey.
Curious about what stock investment entails? Stock investment involves purchasing shares of a company, with the goal of earning a return on your investment. Understanding the fundamentals of stock investing, such as market analysis and portfolio diversification, is key to making informed decisions.