Fundamental analysis for stocks encompasses a crucial aspect of investing, providing investors with essential tools to evaluate the financial health and potential of a company. Exploring the key components and financial ratios, this analysis delves deep into understanding how industry trends and market factors can influence stock valuation.
Understanding Fundamental Analysis

Fundamental analysis for stocks involves evaluating the financial health and performance of a company to determine its intrinsic value and potential for growth. This analysis focuses on key financial metrics, such as revenue, earnings, assets, liabilities, and cash flow, as well as qualitative factors like industry trends, competitive positioning, and management quality.
Importance of Fundamental Analysis in Stock Investing
Fundamental analysis is crucial for investors looking to make informed decisions about which stocks to buy or sell. By analyzing the underlying factors that drive a company’s value, investors can identify undervalued or overvalued stocks, assess the long-term growth potential of a company, and manage risk more effectively.
- Helps in identifying investment opportunities: Fundamental analysis helps investors identify companies with strong fundamentals that are likely to outperform the market in the long run.
- Assists in valuation: By analyzing financial statements and performance metrics, investors can estimate the intrinsic value of a company’s stock and determine whether it is trading at a discount or premium.
- Supports decision-making: Fundamental analysis provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health, competitive position, and growth prospects, enabling investors to make more informed investment decisions.
Difference Between Fundamental Analysis and Technical Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating the intrinsic value of a company based on its financial performance and market position, while technical analysis relies on historical price data and market trends to forecast future price movements. While fundamental analysis is more suited for long-term investors looking to hold stocks for an extended period, technical analysis is often used by traders seeking to profit from short-term price fluctuations in the market.
Fundamental analysis is like looking under the hood of a car to assess its engine and performance, while technical analysis is like analyzing the car’s speed and direction based on the road it has traveled.
Key Components of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating various aspects of a company to determine its intrinsic value. Key components analyzed in fundamental analysis include financial statements and the company’s management team.
Financial Statements
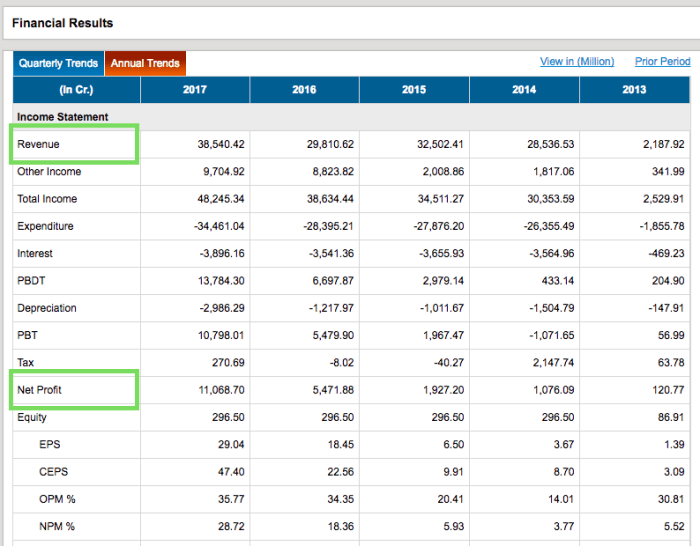
Financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, play a crucial role in fundamental analysis. These statements provide valuable information regarding a company’s financial health, performance, and profitability. Analysts use these statements to assess revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flow to make informed investment decisions.
- Income Statement: Shows a company’s revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period.
- Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a particular point in time.
- Cash Flow Statement: Reflects the cash generated and used by a company during a given period.
Company’s Management Team, Fundamental analysis for stocks
Evaluating a company’s management team is another critical component of fundamental analysis. The effectiveness and integrity of the management team can significantly impact a company’s long-term success. Analysts assess the experience, track record, decision-making skills, and transparency of the management team to gauge their ability to drive the company forward.
It is essential to trust the management team’s ability to make strategic decisions and lead the company in the right direction.
Financial Ratios in Fundamental Analysis

Financial ratios are essential tools used in fundamental analysis to evaluate a company’s financial health and performance. By analyzing these ratios, investors can gain insights into various aspects of a company’s operations and make informed decisions regarding investment opportunities.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios are used to assess a company’s ability to generate profits relative to its revenue, assets, and equity. Some important profitability ratios include:
- Return on Equity (ROE): Calculated as net income divided by shareholders’ equity, ROE measures the return generated on shareholders’ investments.
- Profit Margin: This ratio indicates the percentage of revenue that translates into profit after accounting for expenses.
- Gross Margin: Reflecting the profitability of a company’s core business activities, gross margin is calculated as gross profit divided by revenue.
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios help assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations. These ratios provide insights into the company’s liquidity position and its ability to cover immediate liabilities. Examples of liquidity ratios include:
- Current Ratio: Calculated as current assets divided by current liabilities, the current ratio indicates the company’s ability to cover short-term obligations with its current assets.
- Quick Ratio: Also known as the acid-test ratio, it measures the company’s ability to meet short-term liabilities using its most liquid assets.
- Cash Ratio: This ratio compares a company’s cash and cash equivalents to its current liabilities, providing a more stringent assessment of liquidity.
Fundamental Analysis Tools and Techniques: Fundamental Analysis For Stocks
Fundamental analysis utilizes a variety of tools and techniques to evaluate the financial health and performance of a company. These methods help investors make informed decisions when it comes to buying or selling stocks.
Valuation Methods: Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is a valuation method used in fundamental analysis to estimate the value of an investment based on its expected future cash flows. This technique involves forecasting the future cash flows of a company and discounting them back to their present value using a discount rate. The resulting figure represents the intrinsic value of the investment, which can then be compared to the current market price to determine whether the stock is undervalued or overvalued.
DCF = CF1 / (1+r)^1 + CF2 / (1+r)^2 + … + CFn / (1+r)^n
Qualitative Analysis Methods: SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a qualitative tool used in fundamental analysis to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing a company. By examining these internal and external factors, investors can gain a better understanding of the company’s competitive position and growth potential. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors, while opportunities and threats are external factors that can impact the company’s performance.
- Strengths: Identify the core competencies and advantages of the company.
- Weaknesses: Highlight areas where the company may be lacking or at a disadvantage.
- Opportunities: Explore potential avenues for growth and expansion.
- Threats: Identify external risks and challenges that could affect the company’s performance.
Industry and Market Analysis

Industry and market analysis play a crucial role in fundamental stock analysis as they provide insights into the external factors that can impact a company’s performance and valuation. Understanding the industry dynamics and market conditions helps investors make informed decisions about the potential risks and opportunities associated with investing in a particular stock.
Importance of Industry and Market Analysis
Industry and market analysis help investors gauge the competitive landscape in which a company operates. By analyzing industry trends, market demand, and competitive forces, investors can assess the growth potential and profitability of a company. Moreover, market analysis helps investors understand the overall economic conditions and how they might affect the company’s performance.
- Industry analysis provides information on factors such as market size, growth rate, and barriers to entry that can impact a company’s competitive position and long-term success.
- Market analysis helps investors identify trends, such as consumer preferences, technological advancements, and regulatory changes, that can influence a company’s revenue and profitability.
- By conducting industry and market analysis, investors can better evaluate the risks and opportunities associated with investing in a particular stock and make more informed investment decisions.
Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on Fundamental Analysis
Macroeconomic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, can have a significant impact on fundamental analysis. These factors influence consumer spending, business investment, and overall market conditions, which in turn affect a company’s financial performance and stock valuation.
- Changes in interest rates can impact borrowing costs, consumer spending, and investment decisions, which can affect a company’s revenue and profitability.
- Inflation can erode purchasing power, increase production costs, and affect pricing strategies, leading to changes in a company’s profitability and valuation.
- Economic growth or recession can influence consumer demand, employment levels, and business expansion, all of which can impact a company’s sales and earnings growth.
Influence of Industry Trends on Stock Valuation
Industry trends, such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences, can have a direct impact on a company’s stock valuation. Understanding these trends allows investors to anticipate future challenges and opportunities that may affect a company’s financial performance.
- For example, the rise of e-commerce has transformed the retail industry, leading to the decline of traditional brick-and-mortar stores and the growth of online retailers like Amazon.
- Technological innovations in renewable energy have disrupted the traditional energy sector, creating opportunities for companies focused on sustainable energy solutions.
- Regulatory changes, such as new environmental regulations or tax policies, can impact industries like healthcare, banking, and energy, influencing stock prices and valuations.
In conclusion, fundamental analysis serves as a fundamental cornerstone for investors, offering a comprehensive framework to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving stock market landscape. By mastering the tools and techniques discussed, investors can navigate the complexities of stock investing with confidence and clarity.
When it comes to investing in stocks, understanding how to read stock charts is crucial for making informed decisions. By analyzing patterns and trends, investors can anticipate market movements and identify potential opportunities. To learn more about how to read stock charts effectively, check out this comprehensive guide on How to read stock charts.
For beginners looking to venture into stock investing, having a solid foundation is key. A beginner’s guide to stock investing can provide valuable insights on how to get started, the different types of investments available, and strategies for building a diversified portfolio. Explore this guide to gain a better understanding of stock investing: Beginner’s guide to stock investing.
With the rise of online trading platforms, buying stocks online has become more accessible to individual investors. Understanding how to buy stocks online is essential for executing trades efficiently and taking advantage of market opportunities. Discover the step-by-step process of buying stocks online by following this detailed guide: How to buy stocks online.