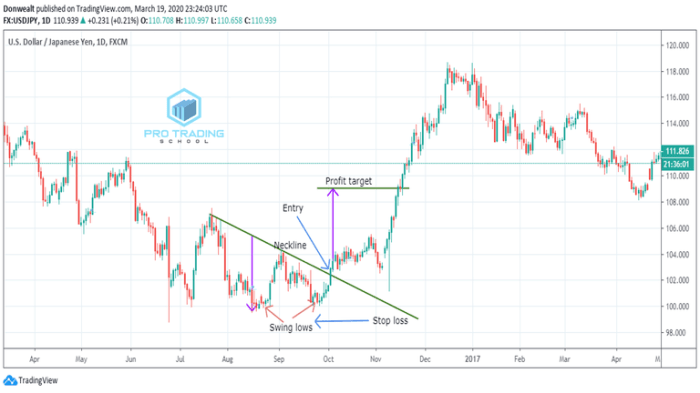
Swing trading stocks is a dynamic strategy that involves buying and selling stocks within a short timeframe to capitalize on market fluctuations. This method requires a keen understanding of market trends and indicators to make informed decisions swiftly.
As we delve deeper into the world of swing trading stocks, we uncover the essential tools, strategies, and real-life examples that can guide you towards success in this high-paced trading environment.
Overview of Swing Trading Stocks
Swing trading is a trading strategy that involves buying and selling stocks within a short to medium-term timeframe, typically holding positions for a few days to several weeks. This strategy aims to capture short-term price movements or “swings” in the market.
Key Characteristics of Swing Trading
- Swing traders typically analyze technical indicators and chart patterns to identify entry and exit points for trades.
- Positions are usually held for a shorter duration compared to traditional buy-and-hold investing.
- Risk management is crucial in swing trading, with traders setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Swing traders aim to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations rather than long-term trends.
Examples of Successful Swing Trading Stocks
- Apple Inc. (AAPL): Apple’s stock has shown consistent price swings based on product launches, earnings reports, and market sentiment, providing opportunities for swing traders.
- Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN): Amazon’s stock has a history of volatile price movements, making it attractive for swing traders looking to profit from short-term fluctuations.
- Tesla Inc. (TSLA): Tesla’s stock is known for its sharp price swings driven by Elon Musk’s tweets, production updates, and market speculation, offering potential opportunities for swing traders.
Tools and Indicators for Swing Trading

Swing traders rely on various tools and indicators to make informed decisions and maximize their profits in the stock market. These tools help traders analyze market trends, identify entry and exit points, and manage risk effectively.
Technical Analysis in Swing Trading
Technical analysis plays a crucial role in swing trading, as traders use historical price data and volume to predict future price movements. By analyzing charts and patterns, traders can identify potential opportunities for profitable trades.
Role of Moving Averages and Relative Strength Index (RSI) in Swing Trading
Moving averages and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) are two key indicators used in swing trading to assess the strength and direction of price trends.
- Moving Averages: Moving averages help traders smooth out price data and identify the overall trend. The most commonly used moving averages in swing trading are the 50-day and 200-day moving averages. Traders look for crossovers between these moving averages to signal potential entry or exit points.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. Traders use the RSI to determine overbought or oversold conditions in the market. A reading above 70 indicates overbought conditions, while a reading below 30 indicates oversold conditions.
Developing a Swing Trading Strategy: Swing Trading Stocks

Creating a personalized swing trading strategy is crucial for success in the stock market. Here’s how you can develop your own strategy:
Setting Entry and Exit Points
- Define clear entry and exit points based on technical analysis, such as support and resistance levels, moving averages, and chart patterns.
- Consider using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit orders to secure profits.
- Adjust your entry and exit points based on market conditions and the risk-reward ratio of each trade.
Identifying Potential Swing Trading Opportunities
- Scan the market for stocks with high volatility and liquidity, as these are ideal for swing trading.
- Look for stocks that are trending strongly in a particular direction, as this increases the probability of a successful trade.
- Use technical indicators like MACD, RSI, and Bollinger Bands to confirm potential entry and exit points.
Risk Management in Swing Trading

Effective risk management is crucial in swing trading to protect capital and maximize profits. Traders must implement strategies to minimize potential losses and control risk exposure.
Importance of Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are essential tools in swing trading as they help traders limit their losses by automatically selling a stock when it reaches a predetermined price level. This prevents emotional decision-making and ensures that losses are kept within acceptable limits.
Risk-Reward Ratios
Risk-reward ratios play a key role in risk management in swing trading. By setting a target profit level before entering a trade and comparing it to the potential loss, traders can assess whether the trade is worth taking based on the risk-reward ratio. A favorable risk-reward ratio helps traders achieve consistent profitability over time.
Impact of Position Sizing
Position sizing refers to determining the amount of capital to allocate to each trade based on risk tolerance and account size. Proper position sizing can help traders manage risk effectively by ensuring that no single trade significantly impacts their overall portfolio. By diversifying positions and limiting the exposure to any single trade, traders can protect their capital during market fluctuations.
Real-Life Examples of Swing Trading Success
Swing trading success stories can provide valuable insights into the strategies and principles that lead to profitable trades. Let’s explore some real-life examples of individuals who have achieved success through swing trading.
Example 1: John Smith, Swing trading stocks
John Smith, a seasoned swing trader, managed to grow his portfolio by 30% in just six months through strategic swing trading. One of the key factors contributing to his success was his meticulous analysis of technical indicators and chart patterns. By identifying high-probability setups and setting tight stop-loss orders, John was able to minimize his risks and maximize his profits.
Example 2: XYZ Hedge Fund
XYZ Hedge Fund is another notable example of swing trading success. By utilizing a combination of fundamental analysis and technical indicators, the fund was able to generate consistent returns for its investors. The fund’s disciplined approach to risk management and strict adherence to its trading plan played a crucial role in its success.
Lessons Learned
- Patience and discipline are key virtues in swing trading.
- Technical analysis tools and indicators can help identify profitable trading opportunities.
- Effective risk management is essential to protect capital and minimize losses.
- Having a well-defined trading strategy and sticking to it can lead to long-term success.
In conclusion, mastering the art of swing trading stocks can lead to profitable outcomes for those who approach it with discipline and a strategic mindset. By incorporating the right tools, risk management techniques, and learning from successful case studies, traders can navigate the stock market with confidence and precision.
When it comes to investing, knowing how to buy stocks online is essential. It allows you to take advantage of opportunities in the stock market without the need for a traditional broker. By following a few simple steps, such as opening an online brokerage account and researching potential stocks, you can start building your investment portfolio. Check out this guide on how to buy stocks online to get started.
Understanding stock market terminology is crucial for any investor. Terms like “bull market,” “dividends,” and “market cap” can impact your investment decisions. By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you can navigate the stock market with confidence. If you want to learn more about stock market terminology, you can check out this detailed guide stock market terminology.
Stock price is a key indicator of a company’s performance in the stock market. It represents the current value of a single share of a company’s stock. Understanding how stock prices are determined and what factors can influence them is essential for investors. If you’re curious about stock prices and how they work, you can read more about it in this article on what is stock price.